Domingues' Research Group



Palladium Nanoparticles Anchored on Magnesium Organosilicate: An Effective and Selective Catalyst for the Heck Reaction
October 22, 2020
A new and effective palladium catalyst supported on a magnesium organosilicate for application in the Heck reaction is presented. A group of compounds comprising 22 examples were synthesized in moderate to high yields (up to 99%) within a short time. The palladium supported on magnesium organosilicate catalyst was characterized as an amorphous solid by SEM, containing around 33% of palladium inside the solid, and even with this low quantity of palladium, the catalyst was very efficient in the Heck reaction. Besides, based on the Scherrer equation, the crystallite size of the synthesized palladium nanoparticles was ultrasmall (around 1.3 nm). This strategy is a simple and efficient route for the formation of C–C bonds via the Heck crosscoupling reaction.
Review of the Syntheses and Activities of Some Sulfur-Containing Drugs
June 13, 2020
Sulfur-containing compounds represent an important class of chemical compounds due to their wide range of biological and pharmaceutical properties. Moreover, sulfur-containing compounds may be applied in other fields, such as biological, organic, and materials chemistry. Several studies on the activities of sulfur compounds have already proven their anti-inflammatory properties and use to treat diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and HIV. Moreover, examples of sulfur-containing compounds include dapsone, quetiapine, penicillin, probucol, and nelfinavir, which are important drugs with known activities

Synthesis and Biological Activities of a Nitro-Shiff Base Compound as a Potential Anti-Inflammatory Agent
May 30, 2020
In order to discover a new compound having anti-inflammatory activity, a nitro-Schiff base was evaluated. The compound was synthesized and characterized by 1H NMR and 13C NMR. The cytotoxic activity was evaluated in vitro by hemolysis and MTT cell viability assay. To evaluate genotoxicity, the micronucleus assay was performed in vivo. The anti-inflammatory effects of the compound were examined using in vivo models of inflammation such as neutrophil migration assay, paw edema, and exudation assay. The production of NO was also estimated in vivo and in vitro. The data showed that the compound did not induce hemolysis at all the tested concentrations. Similarly, the compound did not induce cytotoxicity and genotoxicity to the cells. The neutrophil migration assay showed that the compound reduced the number of neutrophils recruited to the peritoneal cavity by approximately 60% at all the tested concentrations. In the exudation assay, the compound showed a reduction in extravasation by 24%. The paw edema model demonstrated a significant reduction in the paw volume at all the evaluated time points. The production of NO was decreased both in vitro and in vivo. These results suggest that the nitro-Schiff base compound efficiently inhibited inflammation and might be a good candidate for the treatment of inflammatory-associated conditions.

Efficient palladium‐catalyzed C‐S cross‐coupling reaction of benzo‐2,1,3‐thiadiazole at C‐5‐position: A potential class of AChE inhibitors
March 12, 2020
Palladium‐catalyzed C‐S cross‐coupling reaction for access to arylsulfanyl‐benzo‐2,1,3‐thiadiazole derivatives. A series of unpublished sulfur compounds were obtained using a low catalytic loading of palladium prolinate in short reaction time. Besides, the arylsulfanyl‐benzo‐2,1,3‐thiadiazole derivatives were tested in vitro as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and all compounds exhibited anticholinesterase activity.

[Zn(L‐Pro)2] as a Simple and Efficient Catalyst: A Convenient Route for the Synthesis of Thia‐Michael Derivatives via Green Chemical Approach
December 05, 2019
A simple and convenient route for the synthesis of thia‐Michael products was established using pyrazol‐5(4H)‐one with various thiophenols in the presence of [Zn(L‐Pro)2],an efficient catalyst under mild reaction conditions. The salient features of this methodology are good yields, eco‐friendly catalyst, low catalyst loading and faster reaction times.
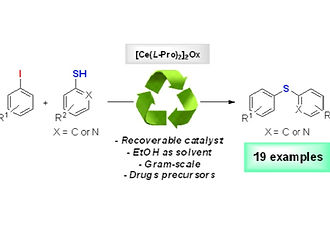
Cerium catalyst promoted C–S cross-coupling: synthesis of thioethers, dapsone and RN-18 precursors
November 06, 2019
In this work, we present a novel, efficient and green methodology for the synthesis of thioethers by the C–S cross-coupling reaction with the assistance of [Ce(L-Pro)2]2Ox as a heterogeneous catalyst in good to excellent yields. A scale-up of the protocol was explored using an unpublished methodology for the synthesis of a dapsone-precursor, which proved to be very effective over a short time. The catalyst [Ce(L-Pro)2]2Ox was recovered and it was shown to be effective for five more reaction cycles.

Cobalt Used as a Novel and Reusable Catalyst: A New and One-Pot Synthesis of Isatin-Derived N,S-Acetals Using Substituted Isatins and Thiols
August 21, 2019
The synthesis of isatin-derived N,S-acetals using cobalt as a recyclable heterogeneous catalyst in batch and continuous flow is reported for the first time. The present protocol produced high yields, which can be observed from the reaction between ketimines and thiols. Such reactions can also be applied to a gram-scale. In addition, the catalyst is recyclable, economically-viable, and nontoxic as well as easy to prepare. The remarkable features of this new methodology are high conversion and cleaner reaction profiles.

A Novel and Efficient Methodology for the Synthesis of Vinylamide Derivatives Using [Ce(L‐Pro)2]2Ox as Heterogeneous Catalyst
June 20, 2018
In this work, we presented a simple, efficient, scalable, and green methodology for the synthesis of arylvinylbenzamides using various anilines and azlactones with [Ce(L-Pro)2]2Ox as heterogeneous catalyst under green conditions in a short reaction time obtained good to excellent yields.

Lipase catalyzed 1,2-addition of thiols to imines under mild conditions
December 20, 2017
This is the first report of enzymes used as a biocatalyst for a 1,2-sulfur addition. In this study, we describe the N,S-acetals synthesis using an environmentally friendly process with low catalyst loading and in short reaction times using lipase pancreas porcine, chymosin, and bovine serium albumin (BSA). The hydrogen bond between the enzyme and the N-Boc imine is a key factor in this reaction.
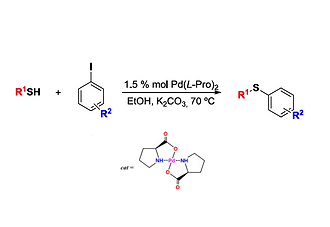
C-S cross-coupling reaction using a recyclable palladium prolinate catalyst under mild and green conditions
September 29, 2017
A simple, efficient and green methodology for the C-S cross coupling reaction using Pd(L-Pro)2 as a heterogeneous catalyst was developed involving aryl iodides, thiols, green-solvent and a low catalytic loading of palladium prolinate. In addition, the catalyst turned out to be recyclable and the products were obtained in good to excellent yields.
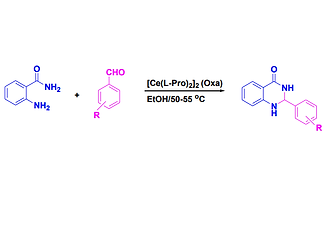
Recyclable [Ce(L-Pro)2]2 (Oxa) used as heterogeneous catalyst: one-pot synthesis of 2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1h)-ones in ethanol
August 24, 2017
[Ce(l-Pro)2]2 (Oxa) was used as a recyclable heterogeneous catalyst under mild conditions for the preparation of 2-aryl-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one derivatives. The one-pot protocol proceeds in ethanol using anthranilamide with several aldehydes at 50–55 °C. The catalyst can be recycled and reused three cycles without significant loss of catalytic activity.

A new procedure for addition of thiols to imines using Zn[(L)-Proline]2 as a catalyst in mild conditions
May 31, 2017
Herein we present a new, highly efficient (60- 98 %), low cost and easy procedure for the addition of thiols to N-Boc imines catalyzed by [Zn(L-Pro)2] aiming the construction of some different N,S-acetals by using a low catalytic loading (1 % mol) in short reactions time and under mild conditions.

[Ce(L-Pro)2]2 (Oxa) as a heterogeneous recyclable catalyst: synthesis of pyrazoles under mild reaction conditions
October 06, 2016
We developed a novel and highly efficient protocol for the synthesis of important pyrazole derivatives by using some 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds and phenyl hydrazines via a one-pot protocol. As a recyclable heterogeneous catalyst, we used [Ce(L-Pro)2]2(Oxa). In addition, the catalyst is recyclable, the proline is economically viable and readily available in both enantiomeric forms and the catalyst is insoluble in almost all solvents and may be easily filtered off from the reaction medium. Moreover, this new synthetic protocol features high conversion, short reaction times, a straightforward procedure and cleaner reaction profiles.
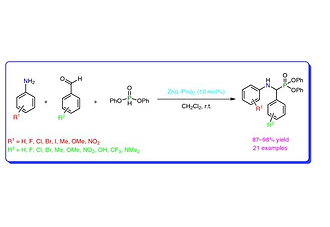
Zinc Di(l-prolinate)-Mediated Synthesis of α-Aminophosphonates under Mild Conditions
September 13, 2016
An efficient method has been developed for the preparation of α-aminophosphonates by using zinc di(l-prolinate) as a catalyst under mild reaction conditions. The method has the advantages of high yields, short reaction times, and easy workup conditions.

A new, efficient and recyclable Ce(L-Pro)]2(Oxa) heterogeneous catalyst used in the Kabachnik–Fields reaction
March 02, 2016
Herein we introduce a new catalyst for the Kabachnik–Fields reaction, [Ce(L-Pro)]2(Oxa), using a very accessible, simple and efficient methodology for α-aminophosphonate synthesis using an aromatic aldehyde, an aromatic amine and diphenyl phosphite. This procedure was developed using a low catalyst loading of cerium(III) prolinate and it has allowed for the recycling of the catalyst.

A novel and efficient methodology for thio-Michael addition in the synthesis of cis-β-thio-α-aminoacid derivatives using Zn[(L)-Pro]2 as heterogeneous catalyst
December 21, 2015
A simple, efficient and green chemical ultrasound assisted thio-Michael addition reaction between thiols and (Z)-azlactones aiming to produce non-natural amino acid derivatives by using chiral Zn[(L)-Pro]2 as a heterogeneous catalyst is herein described. The product was obtained in good to excellent yields presenting high diastereoselectivity.

